Unleash Creativity with Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a cornerstone of creative problem-solving and idea generation. Whether you're working alone or in a team, mastering brainstorming techniques can unlock a flood of innovative ideas. This guide explores the principles of brainstorming, popular methods, and how FunBlocks AIFlow provides the perfect digital environment for effective sessions.
What is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a creative technique designed to generate a large number of ideas around a specific topic or problem in a short amount of time. It emphasizes quantity over quality initially, creating a free-flowing environment where all ideas are welcomed.
Core Principles:
- Defer Judgment: Avoid criticism or evaluation of ideas during the generation phase. All ideas are valid initially.
- Encourage Wild Ideas: Welcome unconventional, seemingly impractical, or "out-there" thoughts. These can spark truly novel solutions.
- Go for Quantity: Aim to generate as many ideas as possible. The more ideas you have, the higher the chance of finding a breakthrough.
- Build on Others' Ideas (Combine & Improve): Encourage participants to combine ideas or suggest variations and improvements on existing ones ("Yes, and...").
Why Brainstorm? The Benefits
Effective brainstorming offers significant advantages:
- Overcomes Mental Blocks: Helps break free from conventional thinking patterns and assumptions.
- Stimulates Group Creativity: Leverages the diverse perspectives and knowledge within a team.
- Explores Possibilities Quickly: Rapidly generates a wide range of potential solutions or approaches.
- Enhances Team Cohesion: Creates a collaborative and energetic environment where everyone contributes.
Common Brainstorming Techniques
There are many ways to brainstorm. Here are a few popular methods:
- Free Association (Classic Brainstorming): Participants call out ideas as they come to mind, often recorded by a facilitator. Focus is on rapid-fire generation.
- Reverse Brainstorming: Instead of asking "How can we solve this problem?", ask "How could we cause or worsen this problem?". Reversing the solutions found can lead to innovative approaches. Useful for identifying potential pitfalls.
- SCAMPER: A checklist method using action verbs to spur ideas: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify (or Magnify/Minify), Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse (or Rearrange). Great for improving existing products or processes.
- Six Thinking Hats: (Often linked with Creative Thinking) Participants metaphorically wear different colored "hats" representing distinct thinking modes (facts, feelings, caution, benefits, creativity, process) to explore a topic from multiple angles systematically. Ensures balanced perspective.
Choose the technique best suited to your specific goal and team dynamics.
The Brainstorming Process & Best Practices
A typical brainstorming session follows these steps:
- Define the Topic/Goal: Clearly state the problem or question you're trying to address. Make it specific.
- Set Rules & Time: Briefly review the core principles (especially defer judgment) and set a time limit for idea generation.
- Warm-up (Optional): A quick, fun creative exercise can help get participants in the right mindset.
- Idea Generation: Use your chosen technique to generate ideas. The facilitator (or participants in a tool like AIFlow) records everything.
- Idea Organization & Evaluation: After the generation phase, group similar ideas, clarify meanings, and then begin the evaluation process (often linking to Critical Thinking methods).
How FunBlocks AIFlow Supercharges Your Brainstorming
FunBlocks AIFlow is tailor-made for dynamic brainstorming sessions:
- Infinite Canvas: Never run out of space! Capture every single idea without worrying about board limits, allowing truly free-flowing thought.
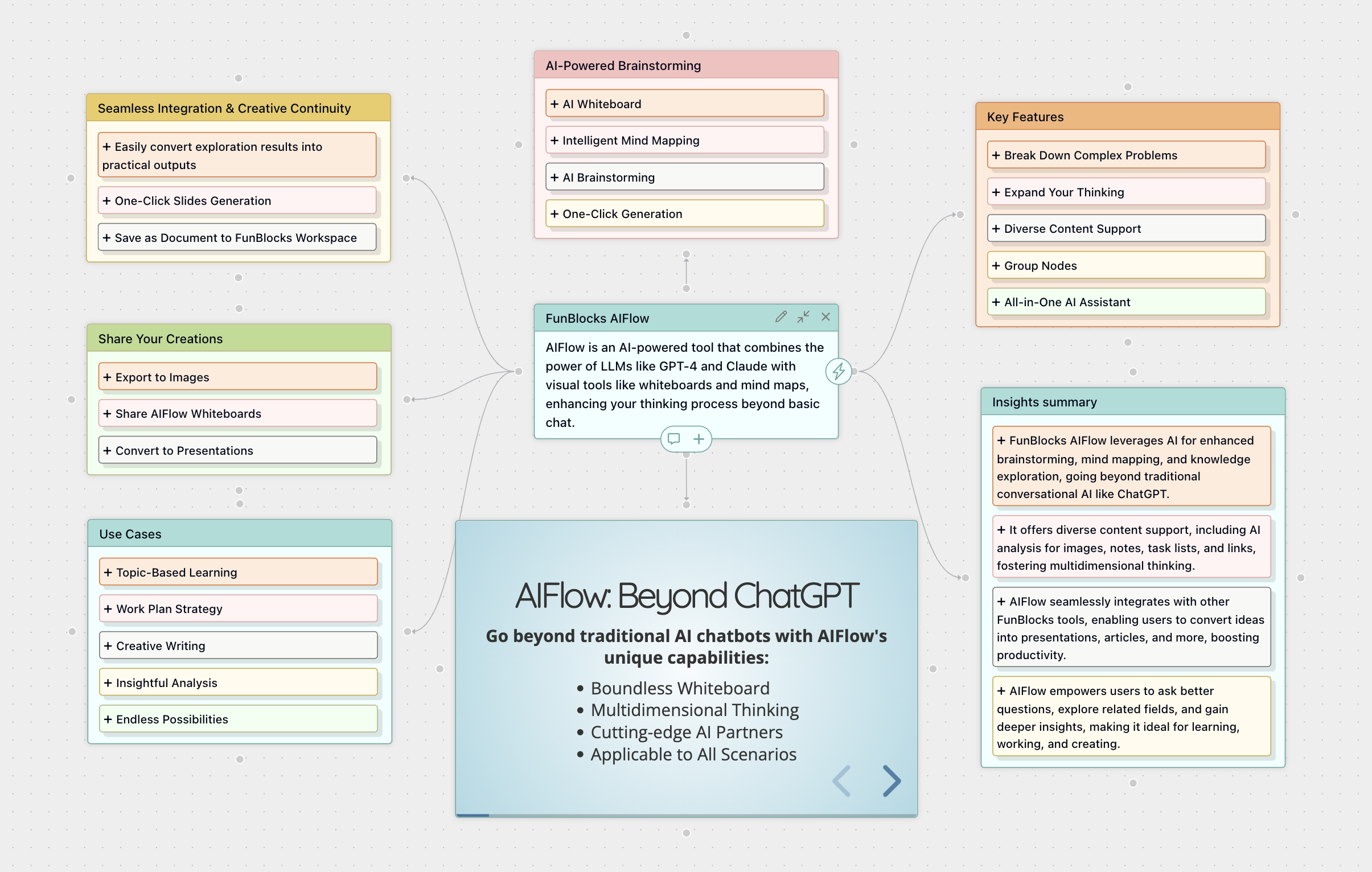
- Digital Sticky Notes/Cards: Quickly jot down ideas on virtual notes. Easily move, group, color-code, and organize them visually.
- Mental Models: Jumpstart your session with pre-built mental models like SCAMPER, Reverse Brainstorming, or basic idea generation.
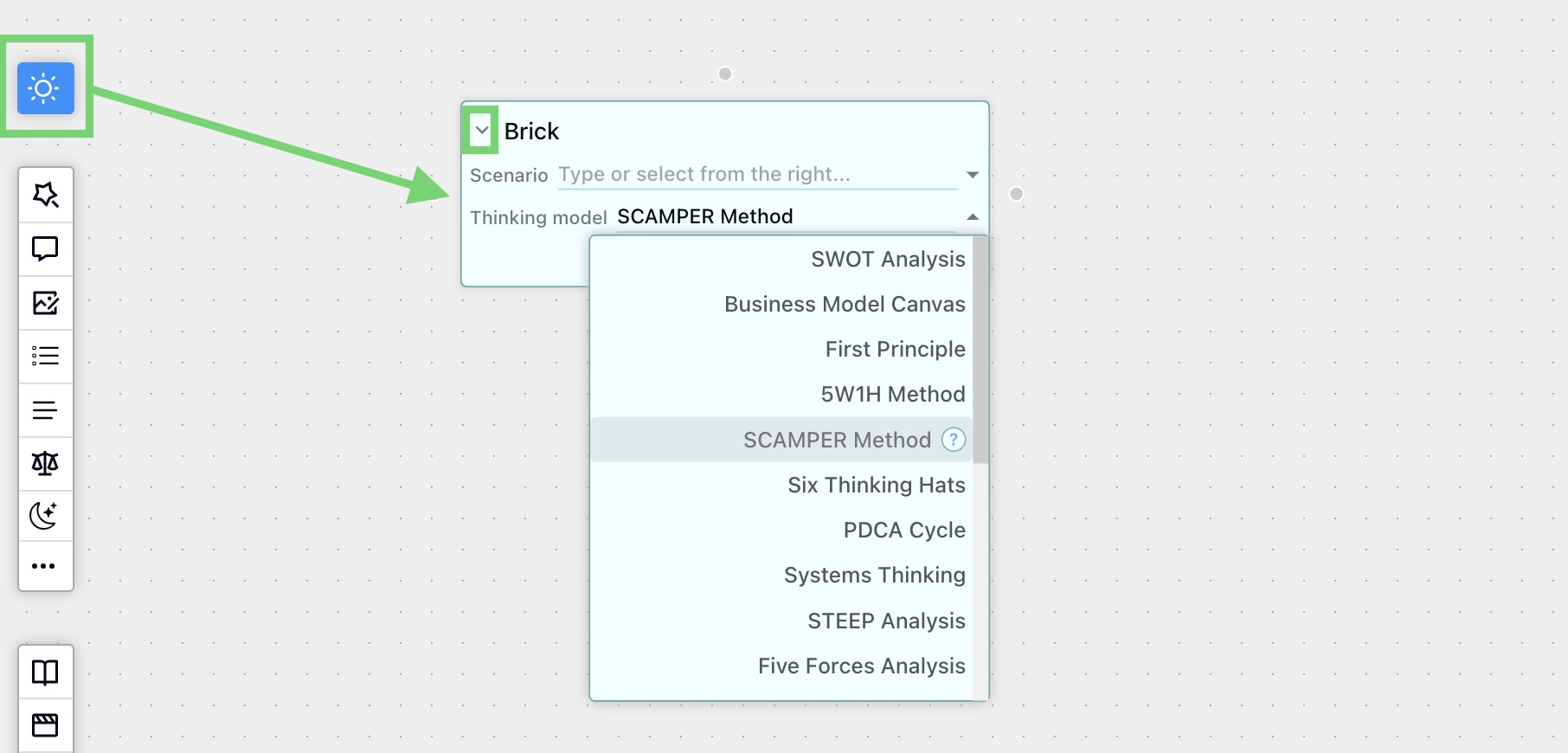
- AI Assistant: Get unstuck with AI-powered suggestions! Generate related terms, ask probing questions, or expand on existing ideas to fuel creativity.
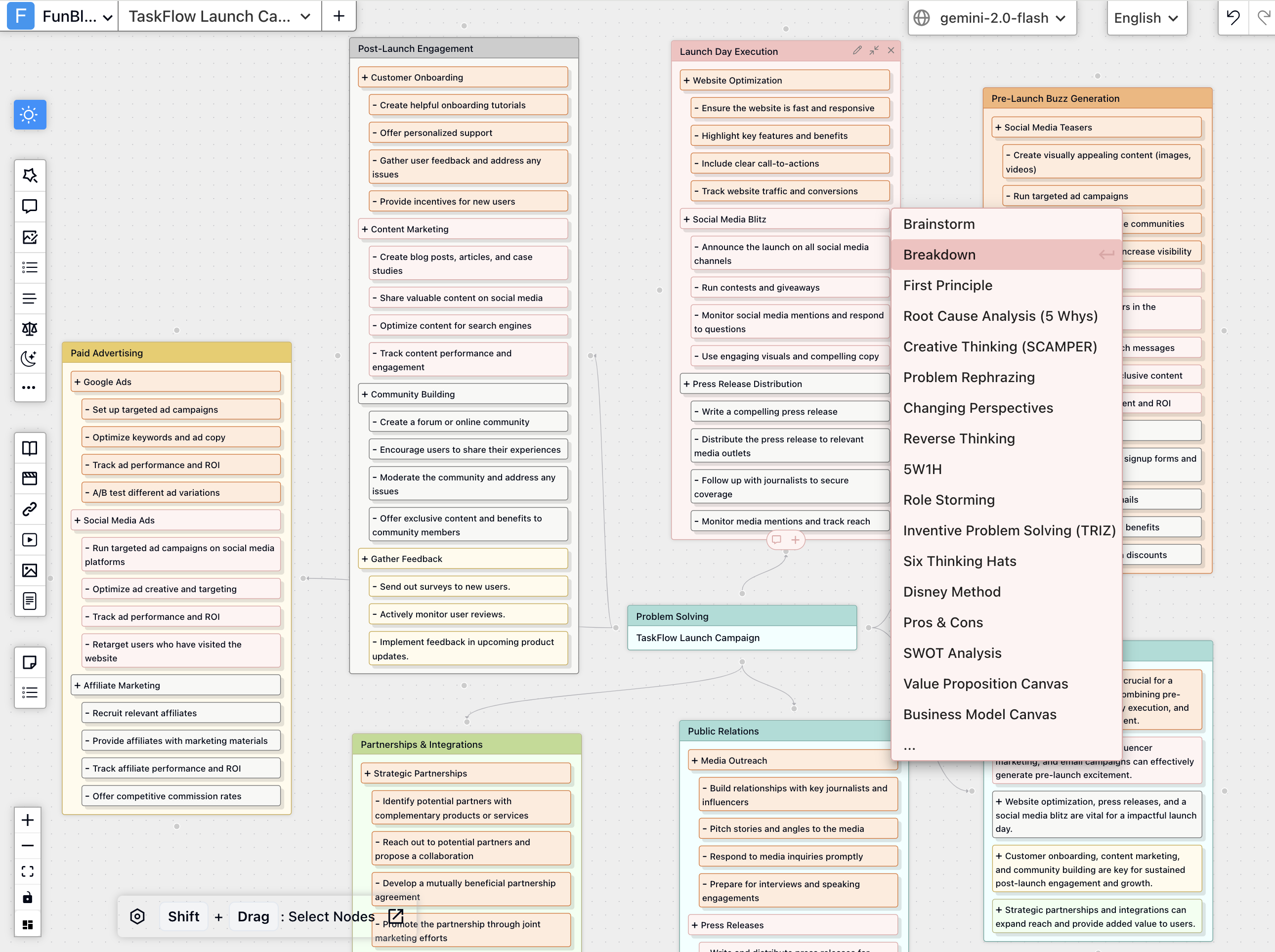
- Grouping: Easily group ideas use visual grouping features (like frames or areas) to start organizing themes as they emerge, simplifying the next phase.
Practice Example: Brainstorming New Product Features with AIFlow
Imagine you need ideas for the next version of your app.
-
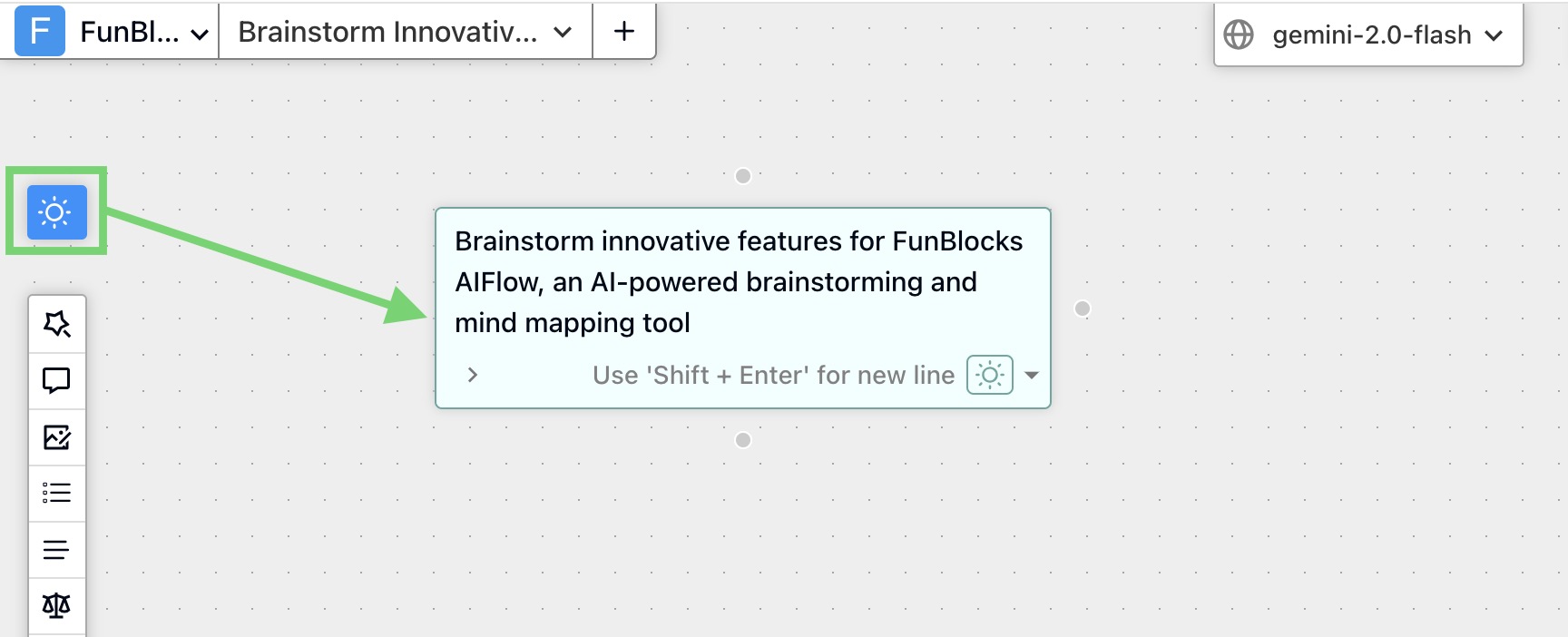
Setup: Create a new FunBlocks AIFlow board and clearly define the goal by titling the board: "Brainstorm Innovative Features for App v3.0".
-
Generate: Add a brainstorming node to the AIFlow whiteboard/canvas. Detail the goal by typing, "Brainstorm innovative features for FunBlocks AIFlow, an AI-powered brainstorming and mind mapping tool..."
-
Next Steps: The generated ideas are now ready for discussion, refinement, and evaluation using critical thinking principles.
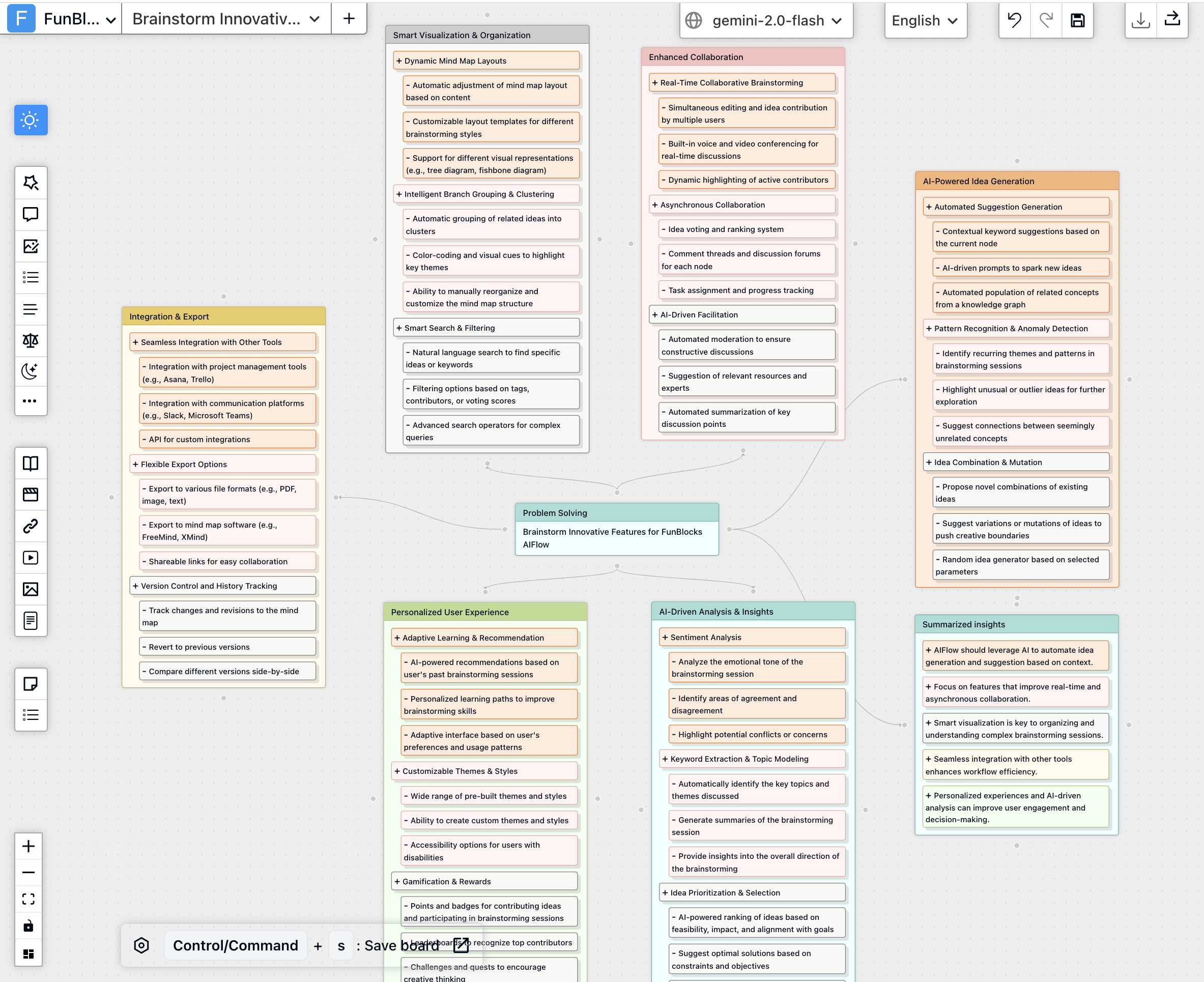
Discover additional brainstorming features in AIFlow: Brainstorming and Ideation with AIFlow
Summary & Tips for Better Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a powerful tool when done right. Remember to:
- Clearly define your focus.
- Strictly enforce the "defer judgment" rule during generation.
- Encourage participation from everyone.
- Use visual/AI tools like FunBlocks AIFlow to generate and organize ideas effectively.
- Don't stop at generation; plan for organizing and evaluating ideas.
Ready to generate some great ideas? Try setting up your next brainstorming session in FunBlocks AIFlow! Next, learn how to organize these ideas visually with Mind Mapping.
Further reading
Brainstorming in the AI Era: Enhancing Creative Problem Solving with Generative AI
Introduction to Brainstorming: Definition and Importance
Brainstorming is a powerful group problem-solving method that generates creative ideas and solutions through spontaneous contributions from team members. This technique involves intensive, free-flowing discussions that encourage every participant to speak openly based on their diverse knowledge and to propose as many ideas as possible. Similar to free writing, brainstorming acts as a pre-writing technique designed to bring subconscious ideas into consciousness, making it particularly valuable when exploring unfamiliar territory or seeking innovative approaches to challenges.
The history of brainstorming traces back to the late 1930s and was popularized by advertising executive Alex Osborn in his 1953 classic book "Applied Imagination." Osborn began developing creative problem-solving methods in the 1930s out of frustration with his employees' inability to independently generate creative ideas for advertising campaigns. He initially called this process "organized ideation," but participants later coined the term "brainstorming session," derived from the concept of "using the brain to storm a problem." Osborn's goal was to reduce social inhibitions among group members, stimulate idea generation, and enhance the group's overall creative thinking capacity.
The importance of brainstorming lies in its ability to encourage more innovative thinking, which is its most obvious benefit. The process requires individuals or teams to think more creatively and without boundaries, leading to better ideas and suggestions. For example, the idea for Amazon Echo reportedly originated from brainstorming strategies. Since brainstorming typically occurs in groups, it forces participants to move beyond their own biases and consider other perspectives without pre-judgment. Furthermore, productive brainstorming exercises not only challenge us to consider alternative ideas but also encourage us to build upon these ideas, resulting in better final outcomes.
Brainstorming also helps develop better teamwork and stronger group cohesion. These collaborative efforts not only produce better ideas but can actually improve team dynamics. Research shows that groups focusing on the quantity of ideas and building on others' thoughts significantly enhance their cohesion. Brainstorming gives everyone an opportunity to be heard and helps teams break free from old, ineffective thinking patterns. This free-flowing ideation technique may produce some seemingly premature ideas, but it can lead to novel and original solutions to complex problems. Brainstorming stands as one of the key strategies for stimulating creativity and solving problems in education, business, industry, and politics.
Core Principles of Effective Brainstorming
Effective creative brainstorming follows several essential principles that maximize its potential for generating innovative solutions:
-
Pursue Quantity: The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible; quantity breeds quality in the realm of creative thinking.
-
Delay Judgment: Pause criticism during the idea generation phase to encourage unusual ideas. Reserve evaluation for later stages to maintain creative flow.
-
Welcome Wild Ideas: Encourage unconventional, "wild" ideas; these often contain the seeds of breakthrough solutions that conventional thinking might miss.
-
Combine and Improve Ideas: Build on others' suggestions; the synergy of combined concepts often produces solutions greater than the sum of their parts.
Additional principles include: visualization of concepts, collaborative building on ideas, and transforming abstract thoughts into actionable tasks. Maintain openness, mutual respect, and a positive atmosphere throughout the session. Take turns speaking, encourage originality, incorporate regular breaks to refresh creative thinking, and keep the process enjoyable. Ensure equal participation opportunities for everyone, encourage free-flowing thought, meticulously record all ideas, and allow time for ideas to incubate. Stay focused on the central topic while maintaining a natural conversational flow.
While Osborn's core principles remain influential, modern interpretations emphasize the importance of collaborative innovation, visual thinking tools, and translating creative ideas into actionable plans. There is some nuanced discussion surrounding the "no criticism" principle, with some research suggesting that constructive feedback in a supportive environment may enhance the creative problem-solving process when properly timed.
Common Brainstorming Methods and Their Applications
Various creative brainstorming techniques have evolved to accommodate different group sizes, personality types (introverted vs. extroverted), and problem complexities:
-
Traditional Brainstorming: Free-form idea generation in a group setting, the classic approach to collaborative creative thinking.
-
Mind Mapping: Visually organizing ideas around a central theme with related concepts extending outward, enhancing understanding of relationships between ideas.
-
Brainwriting: Anonymous written idea generation, followed by sharing and building upon them, reducing social inhibitions.
-
Round-Robin Brainstorming: Each member contributes one idea at a time, ensuring equal participation across the creative thinking process.
-
Reverse Brainstorming: Focusing on problems rather than solutions, asking "How could we cause this issue?" to identify preventative measures.
-
Random Word Brainstorming: Using unrelated words to spark new ideas and break established thinking patterns.
-
5 Whys: Repeatedly asking "why?" to find root causes and deeper insights into complex problems.
-
SCAMPER: Using prompts (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) to explore new possibilities and transform existing ideas.
-
Starbursting: Asking questions (Who, What, When, Where, Why, How) around an idea to explore it thoroughly from multiple angles.
-
Crazy Eights: Drawing eight different ideas in eight minutes to encourage rapid ideation and visual creative thinking.
-
Nominal Group Technique: Anonymous idea generation followed by voting and ranking, reducing conformity pressures.
Recognizing the limitations of traditional brainstorming, various structured techniques have been developed to enhance participation, overcome cognitive biases, and stimulate different types of creative thinking. The shift toward visual methods and digital platforms reflects technological advancements and a deeper understanding of diverse cognitive processes involved in innovation.
The Role of Brainstorming in Innovation and Problem Solving
Brainstorming serves as a foundational technique for innovation and creative problem solving, acting as a catalyst for generating diverse potential solutions. It's important to understand that brainstorming is typically just the first step in a more comprehensive innovation process.
Brainstorming as a Tool for Innovation:
- Creates a free and open environment that nurtures creative solutions
- Facilitates rapid generation of numerous ideas that can later be refined and developed
- Stimulates creative thinking and explores possibilities beyond conventional approaches
Brainstorming's Role in Problem Solving:
- Harnesses the diverse experiences and knowledge of team members
- Identifies a wide spectrum of options and potential root causes
- Generates breakthrough solutions and original ideas that might otherwise remain undiscovered
Brainstorming and Creative Problem Solving (CPS): Brainstorming is a divergent thinking technique focused on generating options, while Creative Problem Solving (CPS) represents a broader process that includes brainstorming but also involves evaluating ideas, refining concepts, and developing implementation plans. Brainstorming typically forms the initial exploratory phase of a comprehensive problem-solving approach.
Innovation demands the generation of novel ideas, and brainstorming facilitates this by emphasizing quantity and suspending judgment during ideation. Problem solving benefits from the different perspectives and range of options that creative brainstorming sessions uncover. Understanding brainstorming as a component within a larger innovation framework provides a more comprehensive view of its strategic role in driving organizational creativity.
Enhancing Brainstorming with Generative AI
In the AI era, brainstorming has evolved significantly with the integration of generative AI technologies that can amplify human creativity and expand the boundaries of innovative thinking:
AI-Powered Idea Generation: Generative AI systems can rapidly produce diverse concepts and perspectives that might not occur to human participants, serving as a digital brainstorming partner that never experiences creative fatigue.
Overcoming Cognitive Biases: AI can help transcend human cognitive limitations by suggesting unconventional connections and ideas untethered from established thinking patterns or group dynamics.
Expanding the Knowledge Base: Generative AI can instantly incorporate vast amounts of information across disciplines, bringing relevant knowledge and analogies from diverse fields into the brainstorming process.
Methods for AI-Enhanced Brainstorming:
-
AI Prompt Engineering: Crafting effective prompts for generative AI that stimulate creative thinking and challenge assumptions. For example: "Generate ten solutions to urban transportation problems that don't involve conventional vehicles."
-
Collaborative Human-AI Brainstorming: Alternating between human ideation rounds and AI-generated suggestions, with each building upon the other's ideas in a creative dialogue.
-
AI-Driven Provocation: Using AI to generate deliberate creative provocations that disrupt conventional thinking patterns, such as suggesting counterintuitive approaches or introducing random elements.
-
Semantic Network Expansion: AI systems can map and expand semantic networks around key concepts, revealing non-obvious relationships and potential innovation spaces.
-
Multi-perspective Simulation: AI can simulate different stakeholder perspectives or thinking styles (similar to de Bono's Six Thinking Hats) to ensure comprehensive exploration of ideas.
The integration of generative AI into brainstorming processes doesn't replace human creativity but rather augments it, providing cognitive diversity and serving as an ideation catalyst. Creative professionals and innovation teams increasingly view AI as a collaborative partner in the creative thinking process, offering complementary capabilities that enhance human ideation.
Tips for Successful AI-Enhanced Brainstorming Sessions
To conduct successful brainstorming sessions with generative AI support:
-
Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for the brainstorming session to provide both human participants and AI systems with proper focus.
-
Prepare Effective AI Prompts: Design thoughtful prompts that guide the AI toward relevant, diverse, and creative contributions to the brainstorming process.
-
Maintain Time Boundaries: Set appropriate time constraints for different phases of the session to maintain energy and focus while allowing sufficient exploration.
-
Balance AI and Human Input: Ensure AI contributions complement rather than dominate human creative thinking, maintaining a collaborative dynamic.
-
Use Visual Organization Tools: Implement digital mind mapping or infinite canvas tools to visually organize the potentially large volume of ideas generated during AI-enhanced sessions.
-
Apply Evaluation Frameworks: Develop systematic approaches to evaluate and prioritize the expanded idea pool that AI-enhanced brainstorming typically produces.
-
Encourage Cross-Pollination: Actively combine human-generated and AI-generated ideas to create hybrid concepts that leverage the strengths of both.
-
Document the Process: Maintain comprehensive records of both the ideas and the pathways that led to them for future reference and pattern analysis.
AI-enhanced brainstorming represents a paradigm shift in creative problem solving, enabling teams to explore solution spaces more thoroughly and efficiently than ever before. The combination of human intuition, domain expertise, and emotional intelligence with AI's pattern recognition, vast knowledge, and unbiased idea generation creates a powerful synergy for addressing complex challenges.
Conclusion: Brainstorming in the Age of AI
The evolution of brainstorming in the AI era marks a significant advancement in collaborative creative thinking. While the fundamental principles established by Osborn remain valuable, generative AI technologies have expanded our capacity for ideation and innovation in unprecedented ways. This technological enhancement doesn't diminish the human element of brainstorming but rather amplifies it, allowing teams to transcend traditional limitations of knowledge, cognitive biases, and group dynamics.
As organizations navigate increasingly complex challenges in a rapidly changing world, the integration of AI into brainstorming processes offers compelling advantages: broader exploration of solution spaces, more diverse idea generation, and faster iteration cycles. The most successful approaches maintain the essence of brainstorming—open, collaborative, judgment-free ideation—while leveraging AI's unique capabilities to enhance creative output.
Looking forward, we can expect further evolution in AI-enhanced brainstorming methodologies, with increasingly sophisticated tools that better understand context, facilitate more natural human-AI collaboration, and provide even more targeted creative assistance. Organizations that master these hybrid approaches to creative problem solving will likely enjoy significant advantages in innovation capability and adaptive response to emerging challenges.
By embracing both the timeless principles of effective brainstorming and the transformative potential of generative AI, today's innovation teams can achieve unprecedented levels of creative thinking and problem-solving success.
Key Takeaways for Enhanced Creative Thinking Through Brainstorming
- Successful brainstorming combines structured approaches with free-flowing creative thinking
- Generative AI serves as a powerful complement to human creativity, not a replacement
- The future of innovative problem solving lies in effective human-AI collaboration
- Organizations should develop specific competencies in AI-enhanced brainstorming techniques
- Creative thinking remains fundamentally human, with AI providing valuable support and expansion
Table 1: Comparison of Common Brainstorming Methods
| Method | Description | Typical Applications | How FunBlocks AIFlow Facilitates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Brainstorming | Free idea generation in groups | Seeking broad ideas, solving open-ended problems | Infinite canvas provides ample space, group nodes can organize ideas |
| Mind Mapping | Visual organization of ideas around a central theme | Knowledge organization, project planning, creative thinking | Provides canvas, easy node creation and connection, color and image support |
| Brainwriting | Anonymous written idea generation, passed around for additions | Avoids groupthink, encourages introverts to participate | N/A |
| Round-Robin Brainstorming | Each member presents one idea in sequence | Ensures equal participation from all members | N/A |
| Reverse Brainstorming | Focus on problems rather than solutions | Identifying potential obstacles, preventing issues | Can set problems as central themes with branches exploring potential issues |
| Random Word | Using random words to spark associations | Breaking thought patterns, generating novel ideas | Can use AI to generate random words, add as nodes to the canvas |
| 5 Whys | Tracing root causes of problems | Deep problem analysis, finding core issues | Can create hierarchical mind maps, layer-by-layer asking "why" |
| SCAMPER | Modifying existing ideas using seven dimensions (substitute, combine, etc.) | Improving products or processes, exploring new possibilities | Can create branches for existing ideas, applying SCAMPER dimensions with AI assistance |
| Starbursting | Asking six key questions around an idea (who, what, etc.) | Comprehensive idea evaluation, discovering potential issues | Can set idea as center, six questions as first-level branches, then expand answers |
| Crazy 8s | Drawing eight ideas in eight minutes | Rapidly generating many ideas | N/A |
| Nominal Group | Anonymous idea generation followed by voting | Avoiding group pressure, objectively evaluating ideas | N/A |