人工智能与高阶思维培养:案例与操作
Outline
Generative AI Key Technologies and Characteristics
Understanding the Core Technologies and Characteristics
A Brief History of AI Development
70 Years Journey from Concept to Reality
Why Now?
Perfect Convergence of Three Key Elements
🔧Computing Power Breakthrough
- GPU parallel computing revolution
- Cloud computing lowering barriers
- Specialized AI chips emerging
📊Data Explosion
- Internet content exponential growth
- Accelerated digitization process
- Mature data annotation techniques
🏗️Technical Architecture
- Transformer revolutionary breakthrough
- Attention mechanism innovation
- End-to-end learning paradigm
End-to-End Learning Paradigm
📖 Core Concept
End-to-end learning is a deep learning approach that directly maps from raw input to final output through a single neural network model, without requiring manual intermediate feature extraction steps.
Core Idea: Let the model autonomously learn the optimal mapping relationship from input to output
⚡ Main Features
- Direct Mapping: Raw data → Deep neural network → Final result
- Global Optimization: Joint training globally, avoiding local optima of sub-modules
- Automatic Feature Learning: No manual feature engineering, model learns representations autonomously
- Task-Driven: Optimization strategy oriented towards the final goal
🚀 Technical Advantages
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Simplified Architecture | Reduce manual design, unified training and inference pipeline |
| Performance Improvement | Achieve SOTA in multiple domains, avoid error accumulation |
| Adaptability | Automatically discover task-relevant features |
| End-to-End Optimization | Global optimization, direct gradient propagation |
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
Understanding the Core Technology of Modern AI
Core Definition
- Generative Pre-trained Transformer: Large language model based on Transformer architecture
- Autoregressive language model: Generates text by predicting the next word
- Unsupervised pre-training + Supervised fine-tuning: Typical representative of two-stage training paradigm
Key Features
- Unidirectional attention mechanism: Can only see previous text, suitable for text generation tasks
- Large-scale parameters: From GPT-1's 117 million to GPT-4's hundreds of billions of parameters
- Powerful zero-shot and few-shot learning capabilities
GPT Core Capabilities and Applications
From Text Generation to Intelligent Reasoning
Text Generation Capabilities
- Creative writing: Stories, poetry, script creation
- Technical documentation: API docs, user manuals, technical reports
- Marketing content: Ad copy, product descriptions, social media content
Understanding and Reasoning
- Reading comprehension: Answering complex text-based questions
- Logical reasoning: Solving mathematical problems and logic puzzles
- Knowledge Q&A: Cross-domain encyclopedic knowledge queries
Code Generation
- Program writing: Generating code based on requirements
- Code explanation: Understanding and commenting existing code
- Debugging assistance: Finding and fixing code errors
GPT Technical Advantages and Limitations
Rational Understanding of GPT's Capability Boundaries
Main Advantages
- Strong generalization: One model handles multiple tasks
- In-context learning: Quickly adapts to new tasks through examples
- Creative output: Generates novel and useful content
Current Limitations
- Hallucination issues: May generate seemingly reasonable but actually incorrect information
- Knowledge cutoff: Training data has time limitations
- High computational cost: Inference requires significant computational resources
- Poor interpretability: Difficult to understand model's decision-making process
Characteristics of Generative AI
From Recognition to Creation
🆚 Differences from Traditional AI
| Traditional AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|
| Recognition & Classification | Content Creation |
| Rule-driven | Data-driven |
| Specialized Systems | General Capabilities |
| Deterministic Output | Probabilistic Generation |
🔗 Core Related Technologies
- Deep Neural Networks
- Attention Mechanisms
- Pre-training & Fine-tuning Paradigm
- Reinforcement Learning Alignment
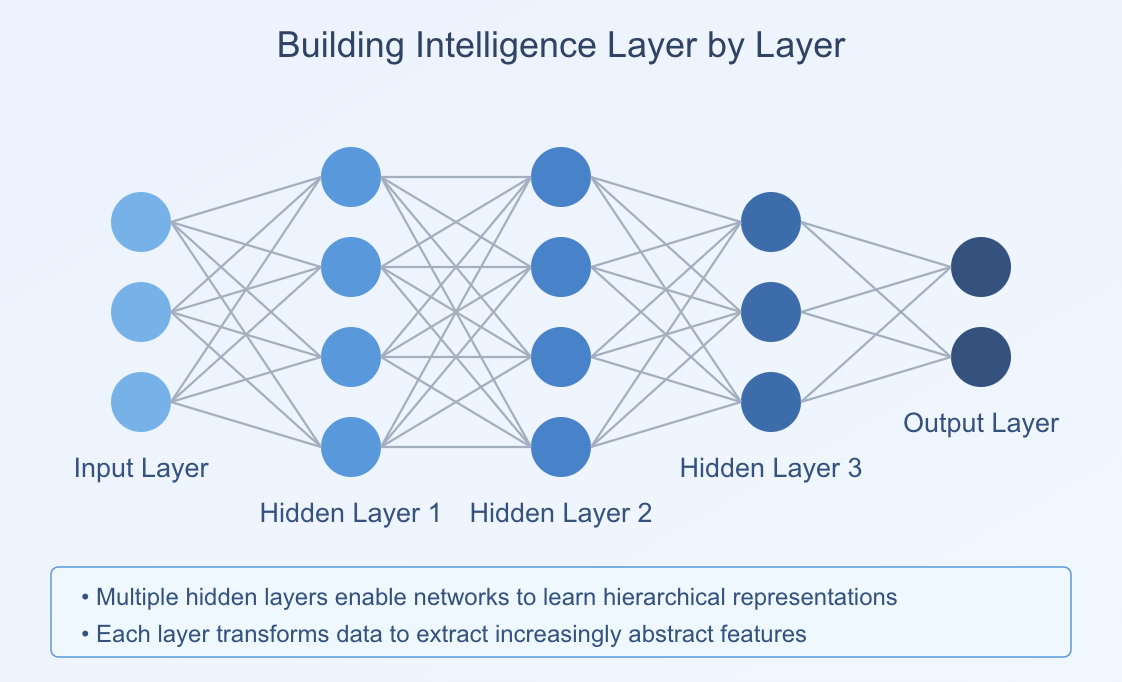
Neural Networks: Mimicking Brain Intelligence
From Biological Inspiration to Artificial Implementation
🧠Biological Neurons
🤖Artificial Neurons
🏗️Deep Networks
🔗 Network Architecture
Parameters, Dimensions, and Tokens Explained
Understanding Core Concepts of Large Language Models
Token
Definition: Token is the smallest unit for model text processing, can be a single character, word, or even part of a word. Created by a tokenizer that splits raw text.
⌨️ Analogy: If you think of a sentence as a wall built with blocks, tokens are each individual block.
Dimensions
Definition: Dimension is the position or "length" of each data point in a vector or matrix. Commonly used to describe the vector space size in hidden layers.
📦 Analogy: If a token is a product, dimensions are the number of "feature labels" it has, like color, size, purpose, etc.
Parameters
Definition: Parameters are the "knowledge" learned by the model during training. They include weights and biases in neural networks.
Scale: GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters, GPT-4 is estimated to have even more.
🧠 Analogy: Think of the model as a brain, parameters are the "memory connections" or "experiences" formed in that brain.
Three Key Stages of AI Training
From Raw to Intelligent Transformation
📚Stage 1: Pre-training
🎯Stage 2: Supervised Fine-tuning
🏆Stage 3: Reinforcement Learning
Mathematical Foundations of AI
Emergence of Intelligence in a Probabilistic World
Probability Theory
Statistics
Optimization
🧮 Core Mathematical Concepts
- Linear Algebra: Vector spaces and transformations
- Calculus: Gradient descent and backpropagation
- Information Theory: Entropy and compression
- Graph Theory: Network structures and relationships
Scaling Law: The Magic of Scale
Bigger is Better?
More Parameters
More Data
More Compute
📊 Scaling Trends
- Performance improves predictably with scale
- Emergent abilities appear at certain thresholds
- But scaling has physical and economic limits
- Efficiency improvements become crucial
Does AI Really 'Understand'?
Statistical Patterns vs True Understanding
Statistical Mastery
Semantic Understanding?
🎭 The Chinese Room Argument
🔬 Current Evidence
- AI shows remarkable language capabilities
- Can reason about abstract concepts
- But lacks grounded experience in the world
- Understanding vs. sophisticated pattern matching remains debated
LLM Hallucination
Models generate seemingly plausible but actually inaccurate or non-existent information
Main Types of Hallucination
Factual Hallucination
- False information: Generating non-existent historical events, people, or data
- Fake citations: Fabricating non-existent academic papers, website links
- Numerical errors: Providing incorrect statistics, dates, quantities
Logical Hallucination
- Reasoning errors: Fallacies in logical deduction
- Causal confusion: Incorrectly establishing causal relationships
- Self-contradiction: Contradictory statements within the same response
Creative Hallucination
- Fictional content: Creating non-existent stories, characters, works
- Mixed information: Incorrectly combining information from different sources
Causes
Training Data Issues
- Errors in training data
- Incomplete training coverage
- Outdated or contradictory information
Model Mechanism Limitations
- Probability-based generation
- Lack of real-world knowledge verification
- Context understanding limitations
Identification and Prevention Strategies
User Level
- Cross-verification: Verify important information from multiple sources
- Critical thinking: Maintain skepticism, especially for specific data
- Professional judgment: Rely on authoritative resources in professional fields
Technical Level
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Combine with real-time knowledge base
- Multi-model verification: Cross-verify using multiple models
- Confidence assessment: Label answer reliability
Can AI Surpass Humans?
Journey Towards Artificial General Intelligence
Current State
AGI Vision
🏆 AI vs Human Capabilities
| Domain | AI Status | Human Level |
|---|---|---|
| Chess/Go | ✅ Superhuman | Surpassed |
| Image Recognition | ✅ Human-level | Matched |
| Language Tasks | 🔄 Approaching | Near human |
| General Reasoning | ❓ Uncertain | Below human |
| Creativity | 🎨 Emerging | Debated |
Human-AI Collaboration in the AI Era
New Capabilities: AI Enhancing Human Achievement
Enhancement Engine: Expanding New Frontiers of Human Achievement
Revolutionizing Scientific Discovery
- AlphaFold: Solved protein folding, predicted 200M+ protein structures, saving ~1 billion years of research time
- MatterGen: "Reverse design" new materials, AI proposes 120K candidate structures in 1 hour
- Scientists evolve from "experimenters" to "hypothesis strategists" and "inquiry designers"
Catalyzing New Renaissance: Arts, Music & Design
- AI Music (MuseNet): Assists composition, arrangement, generates emotion-specific music from text
- AI Art (Midjourney): Lowers visual expression barriers, becomes artists' "creative accelerator"
- Creator value shifts from "technical execution" to "conceptual planning" and "aesthetic judgment"
Personalized World: From Precision Medicine to Customized Experiences
- Precision Medicine: Customized treatment plans based on individual genes and imaging data
- Customized Consumption: E-commerce and streaming create unique experiences for each user
- Adaptive Learning: Dynamically adjusts teaching content based on student progress, achieving "personalized education"
Great Transformation: AI Reshaping Work and Life
Paradigm Shift: From "Job Replacement" to "Task Reconstruction"
Global Labor Market Upheaval
Core shift: From "jobs" to "tasks" - AI automates specific tasks (30%-70%) within jobs, not entire professions.
AI+X Composite Talent
Emergence of "AI+X" professionals who combine domain expertise with AI capabilities, emphasizing lifelong learning for career resilience.
Legal Industry Example
Survival in the AI Era
Adapt to Change, Embrace the Future
Continuous Learning
AI Collaboration
Human Uniqueness
🎯 Strategic Approach
Human Core Competencies: Value Anchors in the Post-Automation World
Value Shift: From "What to Do" to "How to Think and Collaborate"
Higher-Order Cognitive Abilities
- Analytical thinking and creative thinking
- Meta-cognitive skills and learning strategies
Social-Emotional Abilities
- Leadership, collaboration, communication skills
- Empathy, persuasion, and motivation abilities
Personal Traits
- Resilience, flexibility, agility, self-motivation
- AI and big data literacy
Core Metaphor: AI as "Cognitive Exoskeleton"
Cultivating AI Literacy
Technology Should Amplify Human Potential, Not Replace Humans
Understanding AI
Ethical Awareness
Practical Skills
AI Literacy Curriculum
- AI fundamentals and concepts
- Ethical considerations and implications
- Practical AI tools and applications
- Critical thinking and evaluation
- Future trends and developments
How to Communicate Effectively with AI?
From Search Thinking to Conversational Thinking
Treat AI as Human
Unlike traditional keyword search paradigms, AI has intelligence and can understand. Communicate and ask questions in a human way.
Lazy Prompt
When facing more intelligent AI, don't micromanage. Fully leverage AI's capabilities and advantages.
📝 Context
Provide sufficient context information to help AI better understand your needs and background.
- Clarify your role and goals
- Provide relevant background information
- Specify expected output format
- Give specific examples or constraints
Human-AI Four Quadrant Interaction Detailed
Understanding Knowledge Boundaries, Optimizing Collaboration Models
🎯 Four-Quadrant Framework
| Human Knows | Human Doesn't Know | |
|---|---|---|
| AI Knows | Assignment & Validation AI assists with tasks. Humans validate the results to ensure accuracy and reliability. | Query & Discovery AI answers questions and introduces new knowledge, helping expand human understanding. |
| AI Doesn't Know | Teaching & Training Humans teach the AI by providing context and domain knowledge—through SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning) or RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). | Exploration & Innovation Humans and AI collaborate to explore uncharted territory, discovering and creating together. |
💡 Key Insights
- Knowledge boundaries are dynamic, changing with learning and experience
- The most valuable collaboration often occurs in the fourth quadrant (joint exploration of the unknown)
- Effective human-AI collaboration requires both parties to maintain learning and adaptation capabilities
- The goal is to build complementary intelligence, not simple task replacement
Educational Revolution in the AI Era
Rethinking: Educational Revolution in the AI Era
Educational Renaissance: Comprehensive Reshaping of Goals, Content, and Methods
New North Star: Redefining Educational Purpose
- From "knowledge transmission" to "competency cultivation": When knowledge is readily available, education returns to "moral education" essence
- From "knowing" to "becoming": Goal is cultivating "lifelong learners" who can learn autonomously, solve complex problems, and make ethical judgments
- Core competency framework: Countries propose "four-in-one" competency models integrating "knowledge, thinking, values, practice"
Deconstructed Classroom: Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Pedagogical shift: Project-based learning (PBL) and inquiry-based learning as core
- Curriculum reconstruction: From subject-based to competency-based, emphasizing interdisciplinary integration and real-world problem solving
- Learning space transformation: From fixed classrooms to flexible learning environments, supporting personalized and collaborative learning
Broader Educational Transformation in the AI Era
Systematic Changes Across Curriculum, Pedagogy, Roles, and Assessment
Curriculum & Pedagogy Redefinition
- Shift to competency-based and interdisciplinary learning
- Emphasis on "irreplaceable human skills"
- Integration of AI literacy as core curriculum
- Personalized and adaptive coursework
Evolution of Educator & Learner Roles
- Educators as "learning architects" and guides
- Learners as active co-creators and critical consumers
- New skills required: AI literacy, data analysis, ethical guidance
New Pathways in Assessment Methods
- AI-driven formative and summative assessment
- Personalized and adaptive evaluation
- Focus on authenticity, process, and continuous feedback
- Challenge to traditional assessment validity
Human-Centered AI in Education
Dawn of Emerging Educational Concepts
New Paradigms for Human-AI Symbiosis in Learning
Human-AI Co-learning
Humans and AI systems learn together, adapt mutually, and co-evolve through collaboration
- Shared mental models and common ground
- AI as team partner, not just tool
- Mutual learning and adaptation through interaction
Human-Centric AI-First Education (HCAIF)
Prioritizes human values, ethical application, and personalized feedback while leveraging AI capabilities
- AI enhances rather than replaces human capabilities
- Integration of technology, UX, and ethical considerations
- Emphasis on attribution and reflection in AI use
"Machine-Irreplaceable Skills" Philosophy
Focus on developing uniquely human capabilities that AI cannot replicate
- Critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence
- Ethical judgment and complex collaboration
- Human-centered innovation and value-driven outcomes
Epistemological Knowledge & Adaptability
Understanding how knowledge is constructed, validated, and applied in a rapidly changing world
- Meta-cognitive skills and learning strategies
- Adaptability and lifelong learning capabilities
- Integration of programming, data science, complex systems
New Paradigm of Lifelong Learning
From Staged Education to Continuous Growth
Continuous Learning
Just-in-Time Learning
Collaborative Learning
Building Learning Infrastructure
New Tools: AI-Driven Educational Product Ecosystem
From "Content Distributors" to "Cognitive Partners"
Intelligent Tutoring & Adaptive Learning Platforms
Achieve large-scale "personalized education"
Teacher & Administrator "Co-pilots"
AI assists lesson planning, question generation, scheduling, reducing teacher workload and increasing efficiency
Immersive & Experiential Learning Environments
VR/AR virtual experiments, historical scene recreation, enhancing learning engagement
Content Interaction & Analysis Tools
Chat with PDF documents, summarize key points, organize notes
Collaborative Learning Support Platforms
AI-assisted intelligent grouping, discussion guidance, enhancing team collaboration
"Cognitive Gym": Actively Promoting Critical & Creative Thinking
Create and manage "beneficial cognitive friction" rather than pursuing convenience, preventing "cognitive outsourcing"
AI and Higher-Order Thinking Skills Development
Understanding Higher-Order Thinking in the AI Era
From Information Recall to Deep Intellectual Engagement
🧠 What is Higher-Order Thinking?
Higher-order thinking skills encompass sophisticated cognitive processes that distinguish mere information recall from deep intellectual engagement, creativity, and critical analysis. These include analysis, evaluation, and creation—cognitive operations that require examining information critically, making judgments based on criteria, and synthesizing knowledge into novel configurations.
Analysis
Evaluation
Creation
🤖 Reconceptualizing in the AI Era
- Ability to evaluate AI-generated content critically
- Understanding algorithmic limitations and biases
- Maintaining human agency in technology-mediated environments
- Metacognitive awareness of human-AI cognitive interactions
The Cognitive Offloading Phenomenon
How AI Changes Human Thinking Processes
📚 What is Cognitive Offloading?
Cognitive offloading represents the practice of using external tools or resources to reduce mental effort and enhance cognitive performance. This phenomenon encompasses the delegation of memory storage, computation, and increasingly, complex reasoning processes to AI systems.
Traditional Offloading
- Note-taking and external memory
- Calculators for computation
- Maps for navigation
- Preserves higher-order thinking
AI-Era Offloading
- Complex analysis and synthesis
- Creative content generation
- Decision-making support
- May impact skill development
⚠️ Implications for Learning
- Risk of reduced opportunities for sustained analytical engagement
- Potential impact on executive function development
- Questions about intellectual autonomy and adaptability
- Need for balanced human-AI cognitive partnerships
Risk Management: Navigating the Double-Edged Sword
Avoiding Cognitive Outsourcing & Building Co-governance Models
Cognitive Outsourcing Risk
- Paradox: AI is both a "cognitive gym" and potentially a "cognitive crutch"
- Key variable: Impact depends not on AI tools themselves, but on their "pedagogical context"
- Solution: Systematic teacher training to master instructional design that uses AI to promote higher-order thinking
Frameworks for Responsible AI Integration
Systematic Approaches to Preserve Higher-Order Thinking
UNESCO AI Competency Framework
- Human-centered mindset development
- AI ethics understanding
- AI techniques and applications mastery
- AI system design engagement
SchoolAI 4 C's Framework
- Conscientious: Understanding AI capabilities and limitations
- Collaborative: Using AI as a learning partner
- Critical: Evaluating AI outputs critically
- Creative: Leveraging AI for creative purposes
🔄 FunBlocks AI Framework
Unlike traditional human-AI interaction designs that replace human cognition, FunBlocks AI fosters cognitive engagement by posing questions or providing alternative perspectives rather than direct answers. This approach ensures students remain actively engaged in analytical thinking while benefiting from AI's capabilities.
Cases and Operations
FunBlocks AI
Explore, Think and Create with AI
Critical Thinking
Creative Thinking
Boundless Exploration
AI Augmented Thinking
AI-Driven Mental Models Application
Creative Workflows
Key Features
- AI-powered mind mapping and brainstorming
- AI Collaborative thinking spaces
- Integration with mainstream AI models
- AI-powered Critical Analysis
- AI posing questions or providing alternative perspectives
Breaking Through Linear Thinking Limitations
From Chat Thread to Boundless Canvas
Linear Conversation vs Multi-Perspective Exploration
| Linear Conversation | Multi-Perspective Exploration |
|---|---|
| Single-Direction Conversation | Multi-Direction Exploration |
| Single Perspective | Multiple Perspectives |
| Narrower Perspective | Wider Perspective |
| Quick Answer | Deep Thinking |
| Focus on Result | Focus on Process |
Multi-Perspective Thinking Benefits
- Enhanced creativity through multiple perspectives and connections
- Better problem-solving capabilities through multiple perspectives
- Improved learning and retention through critical thinking and visualization
- More comprehensive understanding through multiple perspectives
- Support complex problem decomposition, divide and conquer
Using AI to Enhance Thinking Ability
Let AI Assist Thinking, Not Replace Thinking
AI as Partner
Enhanced Analysis
Creative Catalyst
Thinking Enhancement Strategies
- Use AI for initial idea generation
- Apply human judgment for refinement
- Combine multiple perspectives
- Iterate and improve continuously
- Maintain critical thinking
Summary and Outlook
Embracing Work and Lifelong Learning Transformation in the AI Era
Educational Transformation
Human-AI Partnership
Continuous Adaptation
Key Takeaways
- AI is a tool for enhancing human capabilities
- Focus on developing unique human skills
- Embrace continuous learning and adaptation
- Maintain ethical awareness and responsibility
- Build effective human-AI collaboration
- Shape the future of education with AI